Overview of the Aerospace Industry in Europe and the USA and the Rest Countries
Europe vs. USA: Aerospace Sector Comparison: The aerospace industry is a critical sector that plays a significant role in the economies of both Europe and the USA. Historically, the development of aerospace in these regions has been shaped by various factors, including technological advancements, governmental support, and global competition. In the USA, the aerospace sector can trace its roots back to the Wright brothers’ first flight in 1903, which set the stage for an industry characterized by rapid innovation and military involvement during the World Wars and the subsequent Cold War era. Meanwhile, Europe’s aerospace history began to take shape post-World War II, with nations collaborating to form organizations such as Airbus, which has since become a key player in the global market.
Today, the aerospace industry in the USA is dominated by several major corporations, including Boeing, Lockheed Martin, and Northrop Grumman. These companies are not only known for their commercial aircraft but also for their military and space exploration endeavors. The USA’s aerospace sector is recognized for its high level of investments in research and development, which has propelled it to the forefront of aerospace innovation.
In Europe, the aerospace landscape is equally vibrant, with Airbus being the most prominent player. The European aerospace sector is characterized by a collaborative approach, involving multiple countries and companies, which enhances innovation and efficiency across its operations. Countries like France, Germany, and the UK are central to this collaboration, contributing significantly to manufacturing and technological advancements.
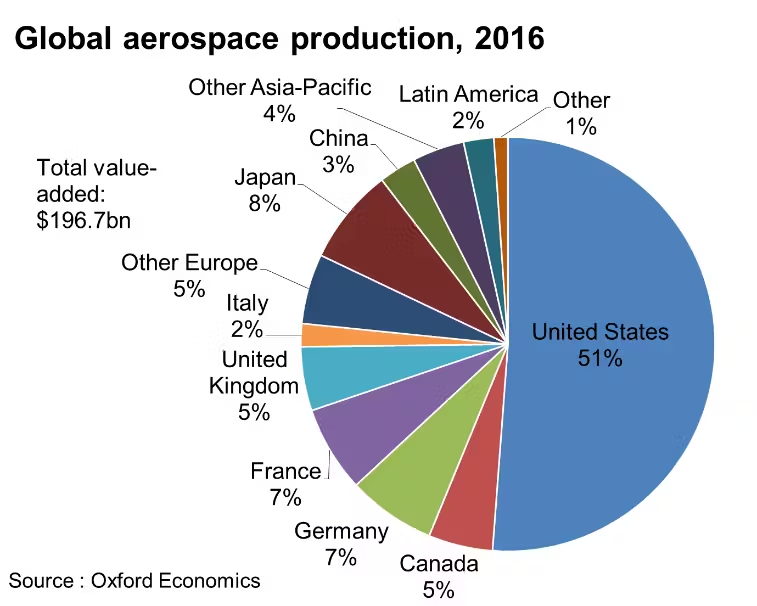
Statistically, the aerospace industry in both regions adds substantial value to their respective economies. In the USA, aerospace accounts for over $900 billion in revenue, while Europe’s aerospace sector contributes approximately €200 billion. Each region holds a significant share of the global market, creating millions of jobs and fostering international trade. This overview highlights the importance of the aerospace industry and its ongoing evolution in both Europe and the USA, setting the stage for future growth and competitiveness in the global arena.
Key Differences in Regulatory Frameworks
The aerospace sectors of Europe and the USA are shaped significantly by their respective regulatory frameworks, which govern safety standards, certification processes, and environmental policies. In Europe, the primary regulatory body overseeing the aviation sector is the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA). EASA was established to ensure a high and uniform level of civil aviation safety across Europe. Its role is pivotal in formulating safety regulations and standards that member states must adhere to, fostering a cohesive regulatory environment throughout the continent.
Conversely, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) oversees aviation in the United States, tasked with regulating all aspects of civil aviation, including air traffic control. The FAA’s certification processes are distinct, often emphasizing innovation and speed in the approval of new technologies. This regulatory difference manifests in the overall pace at which new aerospace products are introduced in the respective markets. While EASA often takes a more conservative approach, prioritizing thorough safety assessments, the FAA may allow for quicker integration of new technologies under certain conditions, impacting manufacturers’ strategies and timelines significantly.
Moreover, the environmental policies associated with aerospace regulation reveal considerable divergence. EASA has been proactive in the formulation of stringent environmental guidelines, pushing for sustainability in aviation. This initiative aligns with the European Union’s broader commitment to reducing carbon emissions and addressing climate change. In contrast, while the FAA also recognizes environmental impacts, its approach has traditionally been more cautious, focusing on balancing safety, innovation, and environmental concerns.
The differences in regulatory frameworks, therefore, create a nuanced landscape for both manufacturers and consumers. Manufacturers must navigate distinct certification processes, impacting development costs and timelines, while consumers may benefit from different safety standards and environmental considerations as these regulations evolve. Understanding these key differences is essential for stakeholders involved in the aerospace sectors across Europe and the USA.
Europe vs. USA: Aerospace Sector Comparison: Research, Development, and Innovation in Aerospace
The aerospace industries in Europe and the United States have distinct approaches to research, development, and innovation, which significantly impact their competitive advantage on a global scale. In the United States, public investment and funding play a crucial role in advancing aerospace technology. NASA, the national space agency, not only funds projects but also collaborates with private sector entities through Public-Private Partnerships (PPP). This collaboration has led to significant advancements in commercial space travel, satellite technology, and aeronautical engineering.
In contrast, European aerospace innovation is characterized by multi-national partnerships, prominently through the European Union’s Horizon programs and initiatives like the Clean Sky partnership. These frameworks emphasize collaboration among various countries, fostering a united approach to technological development. The Airbus consortium exemplifies this cooperative spirit, bringing together expertise from multiple nations to innovate in the aircraft manufacturing sector. The integration of various countries’ resources and knowledge enhances the collective capabilities of European firms.
Investment in educational institutions is another critical factor driving innovation in both regions. The United States has a rich ecosystem of universities and research institutions that specialize in aeronautics and astronautics, including the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and Stanford University. These institutions often engage in groundbreaking research that feeds directly into the aerospace industry. Similarly, European universities engage closely with industries, ensuring a steady pipeline of talent and ideas. Significant projects like the European Space Agency’s (ESA) ambitious initiatives highlight the importance of educational collaboration in driving technological advancement.
Case studies of major advancements illustrate the contrasting approaches in R&D. The development of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) showcases America’s investment in heavy-lift rocket technology, while Europe’s Ariane 6 project represents a concerted effort to maintain competitiveness in satellite launch services.
Market Trends and Future Outlook
The aerospace sectors in Europe and the USA are currently experiencing significant transformations driven by various market trends and future outlooks. One of the most prominent trends includes the increasing collaboration between aerospace manufacturers and technology companies, particularly in developing electric and autonomous aircraft. This partnership aims to enhance the sustainability of aviation while also potentially revolutionizing the travel experience. With heightened awareness about climate change, consumer demand is shifting towards greener technologies, positioning electric aircraft as a viable alternative to traditional jet fuel-powered planes.
In addition to the push for innovative aircraft, advancements in automation and artificial intelligence are reshaping how aerospace operations function. The implementation of autonomous aviation systems, for instance, could streamline operations and improve safety records. However, as these technologies emerge, they necessitate updates to regulatory frameworks to ensure compliance and public safety, which could be a challenge both in Europe and the USA.
Geopolitical factors also play a crucial role in shaping the aerospace markets. Trade agreements, tariffs, and international relations can influence the flow of goods, supply chains, and markets. For example, tensions between nations may result in obstacles for collaboration and increase market volatility. Both regions must navigate these geopolitical landscapes carefully to sustain growth and foster innovation.
Looking ahead, the aerospace sectors of Europe and the USA are poised for growth, with opportunities largely stemming from expanding air travel demand and technological advancements. However, each region faces unique challenges, including workforce shortages and the high costs associated with research and development of next-generation aircraft. By addressing these hurdles while capitalizing on emerging opportunities, both Europe and the USA can secure a formidable position in the future of the aerospace industry.